Human reproductive system
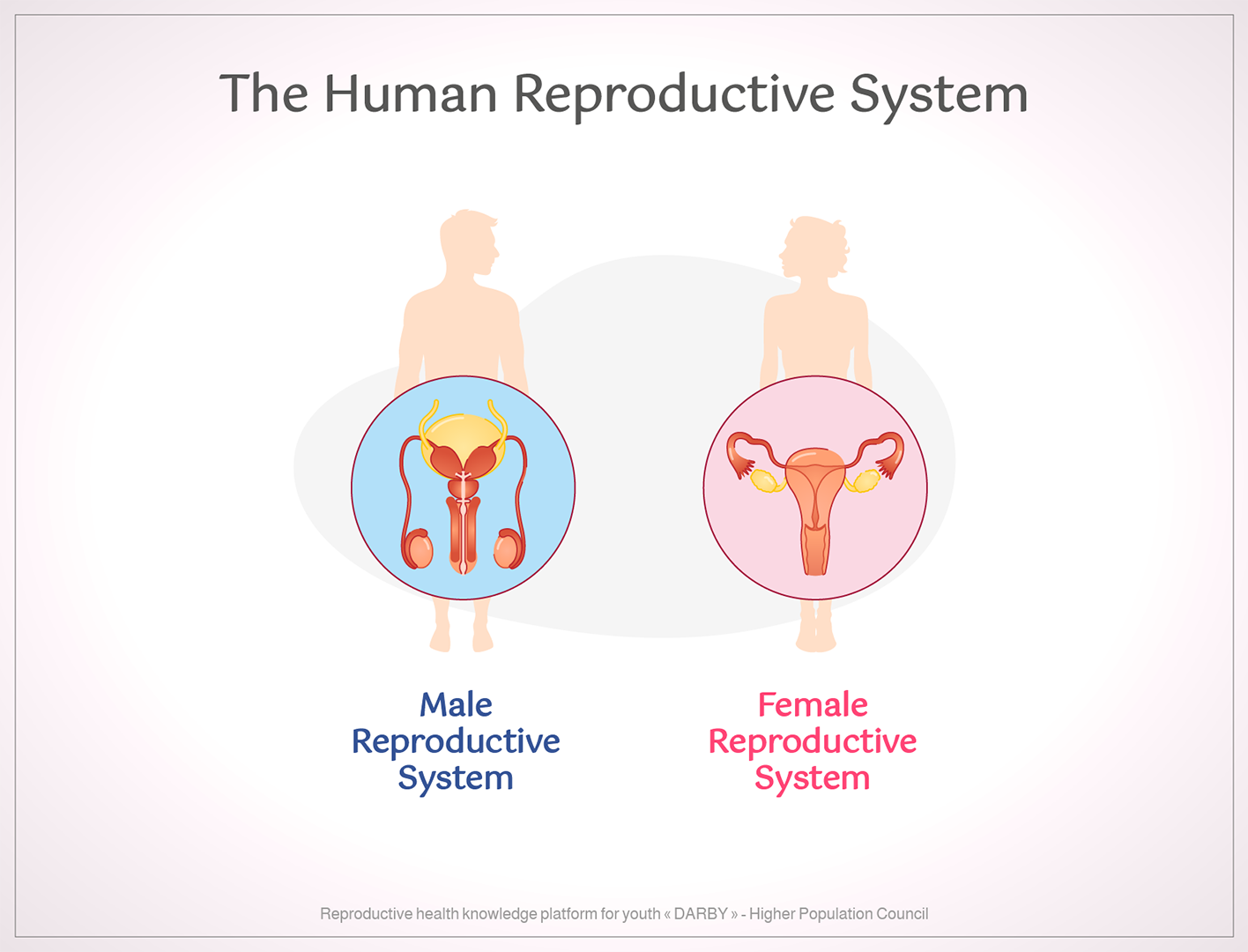
Male reproductive system
Externally
The male reproductive system consists of the penis or male reproductive organ, and the receptacle of the testicles, or scrotum, that keeps the testicles at an appropriate temperature.
Internally
The male internal reproductive system consists of three parts:
The testicles: They are oval and enclosed in a sac called the scrotum. They are the center of sperm production on the one hand and the secretion of male hormones responsible for the development of males and their change at puberty on the other hand.
Ducts: After the sperm is produced in the testicles, it follows a passage called the spermatic cord, and it leaves after a period ranging from two to ten days to months (they are two transport channels, each one of them connected to a testicle through the spermatic cord) connected to the urethra.
Glands: During the passage of the sperm through the various channels and before it reaches the penis, these glands secrete a fluid that nourishes and protects the sperm. This mixture of fluid and sperm is called semen.
.png)
Important Notes:
The urethra is the passage through which urine comes out, as it is the passage through which semen comes out, but all these processes take place at different times and do not coincide.
When you ejaculate, about three milliliters of semen comes out, containing about millions of sperm. As it travels inside the vagina and uterus, many of them die, and only one strong and healthy remains capable of fertilizing an egg if it meets it.
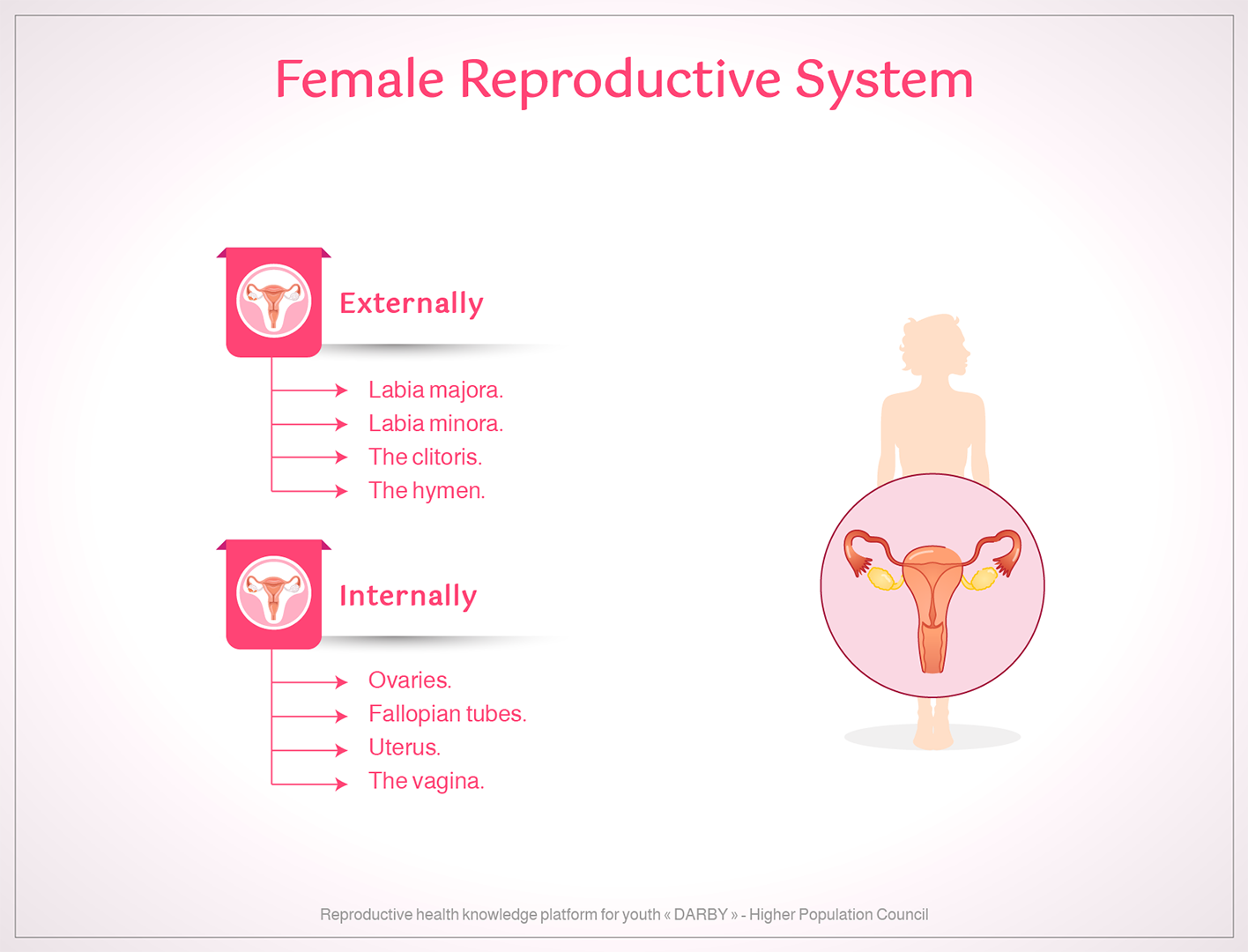
Female reproductive system
Externally
The female reproductive system consists of the pubic bone and its covering tissues, the labia majora, the labia minora, the clitoris, the urethral opening, and the vaginal opening on which the hymen is located from the outside.
The clitoris: It is part of the external genitalia.
The hymen: It is a thin piece of skin located at the beginning of the opening of the vagina. The hymen differs from one girl to another.
Internally
The internal female reproductive system consists of four parts:
Ovaries: The ovaries are in the lower abdomen, with an ovary on each side. It is the center of ovum production as well as the sex hormones that give the female a change in shape at puberty and then secure the production of one ovum every month within the menstrual cycle.
Fallopian tubes: They ensure the transfer of the ovum from the ovary to the uterus because it forms the connection between them. If the sperm meets the ovum inside the fallopian tube, fertilization takes place. Then the fertilized ovum continues its journey to reach the uterus within 4 or 5 days and develops and grows inside it into an embryo. But if fertilization does not occur within 24 hours of the ovulation of the ovum, it will vanish.
Uterus: It is a muscle whose function is to secure the appropriate place and conditions for the growth of the child at the stage of pregnancy. It consists of two parts, the body of the uterus and its cervix.
The vagina: It is a muscular canal that receives the semen through an opening that the penis enters during intercourse and secures the arrival of the semen to the uterus, which is the muscle through which the child passes during childbirth after it is stretched.
Important Notes:
The bladder outlet opening is independent of the vaginal opening, so the channels through which the sperm reach the ovum are separate from the urethra.
The ovary secrets one ovum every month, usually in good health, to be fertilized with a sperm that can pass all the stages to reach the fallopian tube.